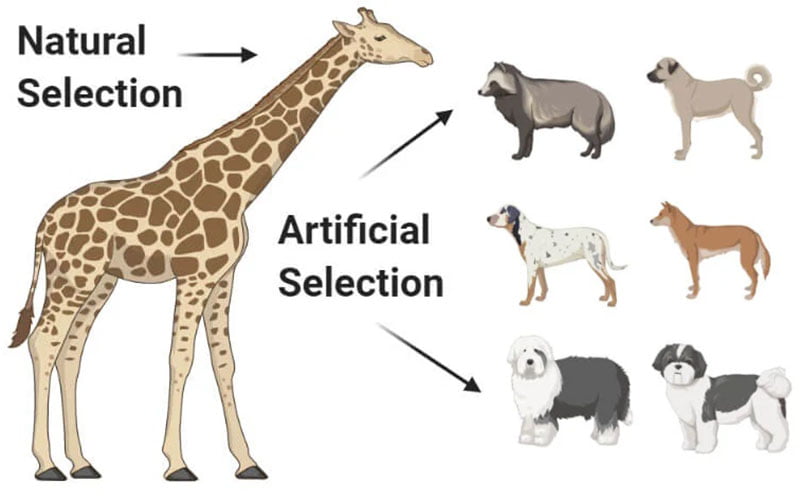
Welcome to an exciting exploration of the concept of artificial selection. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the depths of this fascinating phenomenon, uncovering its meaning, significance, and real-world applications. Artificial selection, also known as selective breeding, is a powerful tool that humans have harnessed to shape the traits of various organisms. By meticulously choosing which individuals to reproduce, we have been able to bring about remarkable transformations in the natural world. So, what is artificial selection, and how does it work? Let’s embark on this captivating journey to find out.
Artificial selection is a process in which humans intentionally select and breed certain individuals with desirable traits to perpetuate those traits in subsequent generations. Through this deliberate manipulation of reproduction, humans have been able to enhance or suppress specific characteristics in plants, animals, and other organisms. By taking advantage of natural genetic variation, artificial selection enables us to shape the evolutionary trajectory of species and create a wide array of variations within a relatively short time span.
Human beings possess a remarkable ability to influence the traits of living organisms through artificial selection. By recognizing and selecting individuals with desirable traits, we have been able to accelerate the process of evolution and bring about changes that would have taken nature thousands of years to achieve. This power of human influence has enabled us to enhance productivity in agriculture, develop specialized breeds of animals, and even breed disease-resistant strains of plants. Artificial selection has undoubtedly revolutionized the way we interact with the natural world.
To understand how artificial selection works, let’s take a closer look at the steps involved:
The first step in artificial selection is identifying the traits that we want to enhance or suppress in a particular species. These traits can be related to physical appearance, productivity, behavior, or any other characteristic that we deem valuable.
Once the desirable traits have been identified, individuals possessing those traits are selected for breeding. These individuals are chosen based on their genetic makeup and the likelihood of passing on the desired traits to future generations.
The selected individuals are bred in a controlled environment, ensuring that they mate with each other and produce offspring with the desired traits. This controlled breeding process allows us to maximize the chances of inheriting the desired characteristics.
The process of artificial selection is iterative, meaning it is repeated over multiple generations. The offspring produced from each round of breeding are evaluated, and the individuals with the most desirable traits are chosen for the next breeding cycle. This continual selection and breeding process gradually amplifies the desired traits while minimizing or eliminating undesirable ones.
This process employed by humans for centuries, resulting in the creation of numerous breeds and varieties of plants and animals. Here are a few notable examples:
The incredible diversity of dog breeds we see today is a result of extensive artificial selection. From the tiny Chihuahua to the majestic Great Dane, each breed has been selectively bred to exhibit specific traits such as size, appearance, temperament, and working abilities.
Through artificial selection, early agricultural communities transformed wild plants into domesticated crops. Wheat, corn, rice, and many other staple crops we rely on today have been selectively bred for improved yield, taste, disease resistance, and other desirable traits.
Pigeon fanciers are using this process of selection for centuries, selectively breeding pigeons to develop distinctive colors, feather patterns, and flight abilities. The diverse array of pigeon breeds we observe today is a testament to the power of artificial selection.
The beauty and variety of roses are a direct result of this process. Over generations, rose enthusiasts selectively bred roses to enhance specific traits such as color, fragrance, petal arrangement, and disease resistance.
A1: Natural selection is a process driven by the environment, where individuals with traits beneficial for survival and reproduction are more likely to pass on their genes to future generations. Where as in artificial selection is guided by human intervention, where individuals with desirable traits are deliberately selected for breeding, irrespective of their natural fitness.
A2: No, it cannot create entirely new species. It can only modify existing species by accentuating or suppressing certain traits. The creation of new species typically requires the accumulation of genetic changes over long periods through natural processes like speciation.
A3: No, it is distinct processes. Artificial selection involves the deliberate breeding of individuals with desirable traits. Where as genetic engineering involves directly manipulating an organism’s genes by inserting, deleting, or modifying specific DNA sequences.
A4: It has been used in the breeding of domestic animals and plants but has not been ethically or practically applied to humans. The idea of selectively breeding humans raises significant ethical concerns and is not practiced in modern society.
A5: This process, like any powerful tool, comes with its own set of risks. Excessive reliance on a narrow set of traits can lead to reduced genetic diversity. Also it makes populations more vulnerable to disease outbreaks or changing environmental conditions. Additionally, unintended consequences can arise when certain traits are prioritized without considering the overall ecological balance.
A6: It plays a significant role in scientific research by providing controlled experimental systems to study the genetic basis of traits. By selectively breeding organisms with known genetic backgrounds, scientists can uncover the underlying genes and mechanisms responsible for specific traits.
Artificial selection is a testament to the incredible influence humans can exert on the natural world. Through our understanding of genetics and the power of selective breeding, we have unlocked the ability to shape the traits of various organisms. From the remarkable diversity of dog breeds to the abundance of crop varieties. Artificial selection has left an indelible mark on our society and the natural world. It is essential to approach this process with a sense of responsibility and ethical consideration. By balancing our desires with the preservation of genetic diversity, we can continue to harness the power of this process for the betterment of our world.
Recommended other topics: Faster Horses: Unleashing Speed, Efficiency And Performance










© InfoDoot. All Rights Reserved.